Reviewed by Alex SmithMay 4 2022
Wireless communications have progressed from 3G to 4G to 5G, and the next phase is underway. What does 6G include, and how will it interact with current infrastructure? Multinational cooperation set out to address these issues, and their findings were published in Intelligent and Converged Networks on April 29th, 2022.
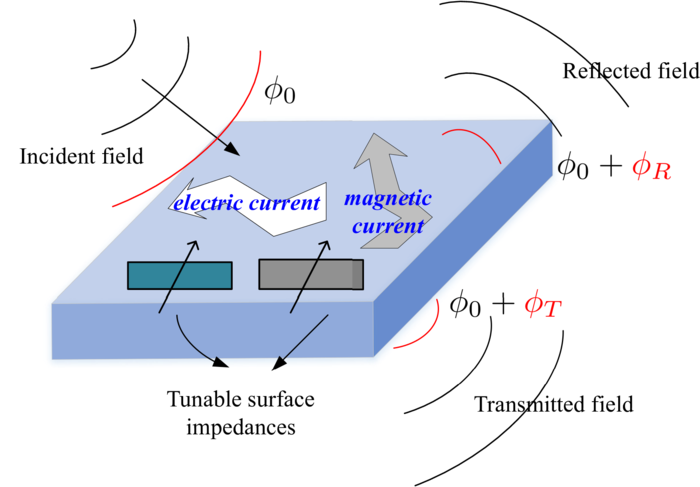 Schematic illustration of the simultaneously transmitting and reflecting RIS element. Image Credit: Intelligent and Converged Networks.
Schematic illustration of the simultaneously transmitting and reflecting RIS element. Image Credit: Intelligent and Converged Networks.
Despite the massive roll-out of 5G networks worldwide, which provide higher flexibility and spectrum/energy efficiency compared to their fourth-generation counterparts, it is inevitable that the sixth-generation—6G—of wireless networks, expected around 2030, and beyond will require more radical communication paradigms, especially at the physical layer.
Ruiqi Liu, Study Author and Master Researcher, Wireless Research Institute, ZTE Corporation
Liu added, “When we review the candidate technologies for next-generation networks, we believe that reconfigurable intelligent surface is among the most promising technologies that will make their way into 5G-advanced and 6G standards and eventually into future networks.”
A reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a planar structure with uniquely programmable components that may be controlled dynamically at any location. For better coverage, the RIS can redirect an incoming signal to exactly reach the intended receiver, or pair it with another for a stronger connection.
According to Liu, the circuits that make up the RIS’s cell units are inexpensive, and because the cells are inactive, the RIS is more energy-efficient than its predecessors.
The incorporation of RISs in wireless networks has been recently advocated as a revolutionary means to transform any wireless signal propagation environment to a dynamically programmable one for various networking objectives.
Ruiqi Liu, Study Author and Master Researcher, Wireless Research Institute, ZTE Corporation
Liu noted, “Currently, the global standards of wireless communications, mainly specified by the 3rd-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) that unites telecommunication standard development organizations to establish the mobile broadband standard, has not explicitly included RIS as a feature.”
“However, RIS can be evolved from the current work on network controlled repeaters and can be deployed in a standard transparent way for current networks—if it is compatible with all current designs and doesn't rely on any new signaling,” explained Liu.
Many 3GPP partners are evaluating RISs in some way, examining and identifying use cases, deployment scenarios, channel models, as well as technical challenges and needs, according to Liu.
Liu’s group looked at the most current advancements in RIS hardware designs and operational factors, as well as the modeling of RISs and RIS-enabled wireless signal propagation. Researchers also discussed channel estimate algorithms for such systems, which may help find the most efficient and secure way to send messages.
Future networks will be greener, more affordable and intelligent because of the advantages RIS can provide, so we highlighted important aspects of RIS in this paper to provide an understanding of this technology and how the wireless network will evolve towards the next generation.
Ruiqi Liu, Study Author and Master Researcher, Wireless Research Institute, ZTE Corporation
Liu stated, “We believe that the current standardization activities will help to mature this technology and pave way to its commercialization in the future. Currently, though, RIS is still a dynamic research topic under study, with many possible options to explore. Many key issues still need to be solved before launching RISs commercially.”
As part of the worldwide standards effort, Liu said the researchers want to look at the important concerns of channel modeling, estimating and feedback in greater depth, as well as examine different hardware designs.
Other authors included Mengnan Jian, Wireless Research Institute, ZTE Corporation; Ertugrul Basar, Communications Research and Innovation Laboratory (CoreLab), Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Koc. University, Turkey; George C. Alexandropoulos, Department of Informatics and Telecommunications, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece.
Some other authors who also contributed to the study is Yuanwei Liu, School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, Queen Mary University of London, England; Chongwen Huang, College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University, China; and Chau Yuen, Engineering Product Development (EPD) Pillar, Singapore University of Technology and Design.
This research was partially funded by the EU’s H2020 RISE-6G program.
Journal Reference:
Jian, M., et al. (2022) Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for wireless communications: Overview of hardware designs, channel models, and estimation techniques. Intelligent and Converged Networks. doi.org/10.23919/ICN.2022.0005.