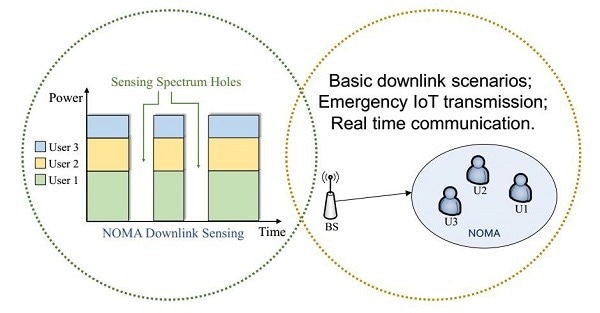
Schematic diagram of downlink hybrid IoT sensing scene and an illustration for frequency band occupancy status. Image Credit: Shanghai Advanced Research Institute
Ensuring the performance of spectrum utilization and system throughput in large-scale IoT scenarios while integrating both technologies at the same time, however, presents significant issues given the complexity of future IoT scenarios.
An innovative spectrum sensing technique for 6G-oriented intelligent IoT communications was creatively proposed by a research team from the University of Windsor in Canada, the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the VTT Technical Research Centre in Finland in response to this challenge.
The team was aiming for a viable technique that would fundamentally aid in perceptual interference and intelligent identification between widespread coexistence and aliasing IoT users in forthcoming 6G scenarios.
The most recent IEEE Internet of Things Journal issue includes the results.
The researchers created a multi-layer spectrum sensing method based on feature detection in NOMA situations with multiple users with an emphasis on inter-system orthogonal/non-orthogonal aliasing coexistence scenarios.
The threshold expressions were derived per the described reasonable transceiver topologies and procedures for various cases.
The researchers created one downlink mode and two uplink modes to define relationships between users’ priority, power, and transmission forms in light of the impending 6G complicated scenarios.
They then tailored the detection probability optimization method based on the unique properties of each mode and scene, enabling the proposed technology to significantly increase the detection probability of orthogonal/non-orthogonal hybrid IoT systems and boost system throughput.
Experimental findings demonstrate the viability of the suggested spectrum sensing method, which also shows excellent detection and throughput capabilities.
The theory of signal perception and recognition for 6G-focused intelligent IoT communications will be advanced by this effort, which will also offer technical support and development opportunities to promote a global 6G strategy.
Journal Reference:
Wu, J., et al. (2022) Feature-based Spectrum Sensing of NOMA System for Cognitive IoT Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. doi:10.1109/JIOT.2022.3204441.