The melt flow rate (MFR) of a thermoplastic material can be calculated using a flow rate test. As outlined in ASDTM 1238, the ‘Method A’ test is where extrudate from the die is collected over a specified time period and under particular load and temperature conditions.
The mass of the extrudate(s) is then used to calculate the mass melt flow rate as per the below equation.
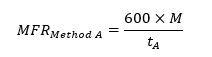
The MFR value is expressed through the units g/10 min (grams extruded per 10 minutes). Sometimes called the ‘cut-n-weight’ method, ‘Procedure A’ is an entirely manual process.
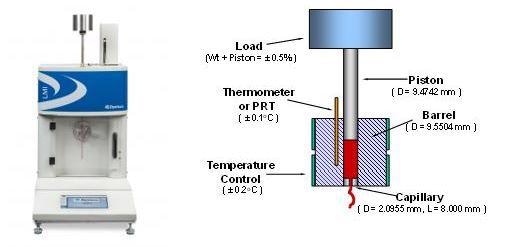
Image Credit: Dynisco
On the other hand, the 'Method B' test is used to evaluate the characteristics of a material’s flow according to the volumetric displacement instead of the weight of extrudate with time as in 'Method A.'
Opposed to 'Method A,' the 'Method B' test does not require weighing or cutting of the extrudate to be effectively performed. The 'Method B' test results can be conveyed directly as Melt Volume-flow Rate (MVR) in cc/10 min.
The apparent melt density determined from the 'Method A to B conversion' is required to relate the results of a 'Method B' test back to 'Method A.' No cuts are involved in a 'Method B' test. As such, it offers higher precision for routine analysis and is simpler to perform.
The volumetric displacement of the extrudate(s) is used to calculate the MVR from 'Method B' as per the below equation:
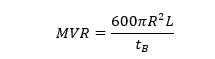
where R is barrel radios (R= 0.477 cm) and tb is the time taken for the piston to travel the distance of L (flag length).In line with ASTM 1238, L is equal to 0.635 cm. The value of ‘600’ has been included to express the MVR in cc/10 min.
The value of the MFR (g/10 min) is determined by multiplying the calculated MVR by the material’s melt density, as shown in the below equation:
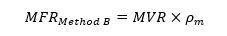
where Pm (g/cm3) is the apparent melt density of the polymer at the test temperature. It is important to note that the polymer’s melt density is the function temperature. Equally, the melt density of the material can be increased by fillers and reinforcing agents, among others.
This test method is advantageous for the quality control of materials from various supplier lots or processes.
MFR is an empirically defined measurement that is impacted by the molecular structure and physical characteristics of the polymer materials, for example, molecular weight, viscosity, moisture in the material, molecular weight distribution, additives, degradation, or crosslinking.
This test can also be used in applications that require certain polymer characteristics to be identified, such as extrudate swell, intrinsic viscosity, thermal stability and shear thinning of the polymer melt.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Azadeh Farahanchi from Dynisco.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Dynisco.
For more information on this source, please visit Dynisco.