Oct 22 2010
Facultad de Informática-based Artificial Intelligence Group (LIA) at Universidad Politécnica de Madrid has developed a novel DNA-supported biosensor that plays a significant role in genetic diagnostics.
The fundamental structure of this unique sensor was revealed at the Unconventional Computation Conference, 2010.
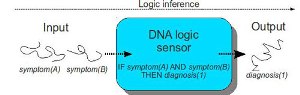 The new system of diagnosis using DNA biosensors
The new system of diagnosis using DNA biosensors
The LIA team has already filed a patent application for this particular structure of the analytical DNA sensing device. These sensors are capable of illustrating the logical representations following the IF-THEN rules; for instance, If symptom 1 and 2 are exhibited, THEN the disease is A, or If the disease is B, THEN symptoms 2 and 3 must be shown. The sensors follow such logical implications to independently execute the logical inference methodologies based on the genetic signals and arrive at precise diagnoses.
By employing these smart DNA sensing units as a fundamental platform, the researchers focused on advancing invitro devices that have the potential to independently determine various input symptoms and generate spontaneous diagnostic methods or discharge the appropriate drug to overcome it.
These DNA-based biosensors are assumed as bionanotechnological solutions and are included in biomolecular computing or DNA computing discipline. This particular stream focuses their work on designing and programming equipments that have been fabricated using biomolecules, for instance, DNA molecules are deployed to process the data that are encoded in various other biological molecules.