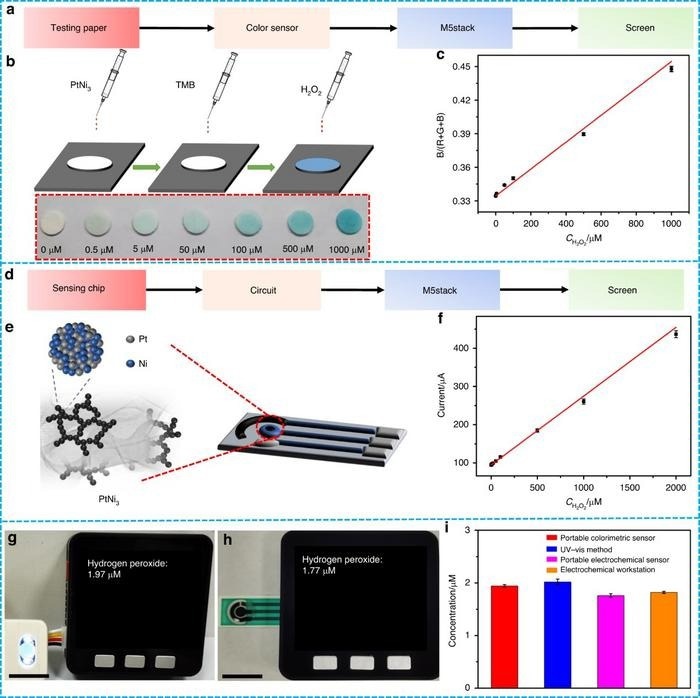
Diagram and application of the portable visual and electrochemical H2O2 sensors. a–c Schematic illustration and corresponding calibration curve of portable visual H2O2 sensing based on testing paper. d–f Schematic illustration and corresponding calibration curve of portable electrochemical H2O2 sensing. g, h Measurement of H2O2 released from HeLa cells with portable visual and electrochemical sensors. Scale bar = 1.0 cm. i Comparison of H2O2 concentrations measured with the portable colorimetric sensor, the UV‒vis spectrophotometer, the portable electrochemical sensor, and the electrochemical workstation, respectively. Image Credit: Microsystems & Nanoengineering
By creating dual-functional portable sensors based on Pt-Ni hydrogels, researchers from Northwestern Polytechnical University (NPU) have made significant progress in the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), an essential biomarker in biological processes. The study was published in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
Personalized healthcare is about to undergo a revolution thanks to these sensors, which are proficient in both colorimetric and electrochemical detection.
The novel Pt-Ni hydrogels, which are produced using a straightforward co-reduction procedure, are essential to a novel H2O2 detection technique. These hydrogels offer a large surface area that is essential for biosensing because of their distinctive structure of crumpled nanosheets and nanowire networks.
They allow for the detection of H2O2 by colorimetric and electrochemical methods and exhibit notable peroxidase-like and electrocatalytic activities. The colorimetric method uses a fast response time and a noticeable color shift in the hydrogel upon interaction with H2O2, which is detectable by UV-visible absorption spectra.
Cyclic voltammetry is used to validate electrochemical sensing, demonstrating the hydrogels' efficiency in reducing H2O2. Important discoveries include wide linearity ranges, remarkable long-term stability of up to 60 days, low detection limits for both colorimetric (0.030 μM) and electrochemical (0.15 μM) approaches, and good selectivity—all necessary for precise H2O2 measurement in complicated materials.
Furthermore, the sensors' ability to identify H2O2 from HeLa cells closely matches that of established spectrophotometric and electrochemical techniques, indicating the possibility of real-world uses.
The field of health monitoring has advanced significantly with the introduction of these portable H2O2 sensors. Because of their selectivity, sensitivity, and ease of use, they are perfect for point-of-care diagnostics, opening up new possibilities for individualized treatment.
These gadgets have the potential to be seamlessly integrated into daily life, which might completely change how we track and manage health issues and open the door to more extensive uses in therapeutic monitoring and medical diagnostics.
Journal Reference
Li, G., et.al., (2024). Portable visual and electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide release from living cells based on dual-functional Pt-Ni hydrogels. Microsystems & Nanoengineering. doi.org/10.1038/s41378-023-00623-y