Imec, a Belgium based nano-electronics technology provider in association with Holst Centre, has revealed an advanced low-power 2.3/2.4 GHz transmitter developed for wireless sensor applications which are compliant with Bluetooth Low Energy and 4g/4/IEEE802.15.6 wireless standards.
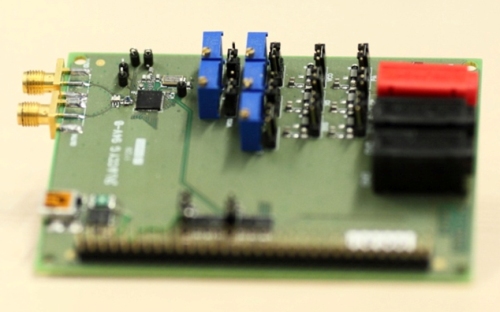 Imec multistandard transmitter
Imec multistandard transmitter
The transmitter consumes 5.4 mW power from a 1.2 V supply at an output of 0dBm. It is more power-efficient than other Bluetooth-Le solutions. The results were acquired in collaboration with Panasonic, as a part of the program for developing ultralow-power wireless communication.
Remote monitoring, logistics, smart building and personal healthcare applications require low-power wireless solutions which are required to operate extended periods on a harvester source or a small battery. For these applications, a 2.4 GHz wireless standard has been defined in the ISM band, including Bluetooth Low Energy, IEEE802.15.4 and IEEE802.15.6. However, these compliant transmitters use from 20 to 50 mW, which is inappropriately high for semi-autonomous or autonomous sensor nodes.
The latest Imec transmitter uses digitally-assisted circuits in place of analog blocks to reduce power consumption by 75%. It makes the new Imec transceiver complaint with all four standards and it requires only 4.5 mA from a power supply of 1.2 V. The resultant multi-standard device can be reconfigured. Demonstrations support the data rates and modules from 50k to 2Mbps.
Imec demonstrated the transceiver at the recently held IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference of 2012.
Headquartered in Leuven, Belgium, Imec has offices in the United States, Japan, India Netherlands, Belgium, Taiwan and China.