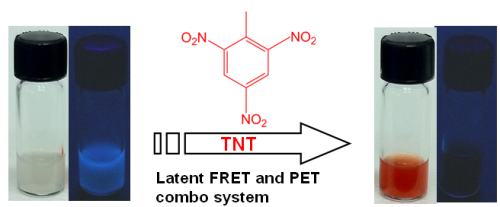
Researchers from the University of Connecticut have developed an explosives detector capable of sensing minute amount of TNT and other explosives present in liquids. At the recently held National Meeting & Exposition organized by the American Chemical Society, the new sensor has been deemed suitable for integration into a TNT test strip.
 A new, ultrasensitive real-time sensor can detect trace levels of explosives, such as TNT, in liquids.
A new, ultrasensitive real-time sensor can detect trace levels of explosives, such as TNT, in liquids.
Offering the high degree of sensitivity offered by bomb-sniffing dogs, the sensor can be used in detecting water contaminated by TNT, caused by obsolete storage facilities, production and other sources.
Developed by researchers, Dr. Yu Lei and Ying Wang, the easy-to-use sensor will now be made even more user-friendly by integrating it with a paper strip, comparable to the test strips used for pregnancy. At airports or checkpoints, the screener can dip the sensor-incorporated filter paper into the liquid sample and check the level of fluorescence, which will determine the presence of TNT or other explosives in real-time. The sensor can also be used in rivers or streams in the vicinity of manufacturing facilities and munitions testing sites to easily detect contamination of water by TNT.
A graduate student in Dr. Yu Lei’s laboratory, Ying Wang stated that the sensor fulfills the demand for an accurate and rapid method for sensing nitroaromatic compounds (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) in fresh water, salt water and other liquid samples. These compounds are widely used in agriculture, military and construction applications and are used as the standard for calculating explosive force. Wang added that to detect the presence of TNT at docks is a major concern and needs to be addressed quickly.
Traditional testing methods requires the sample to be shipped to a state-of-the-art laboratory. The new sensor will enable homeland security and law enforcement officials to determine the presence of TNT instantaneously, since the color change occurs only when the sensing molecule is attached to the explosive. The high sensitivity and large sensing range of the sensor makes it ideal for rapid selective and sensitive detection of explosives in water-based samples.