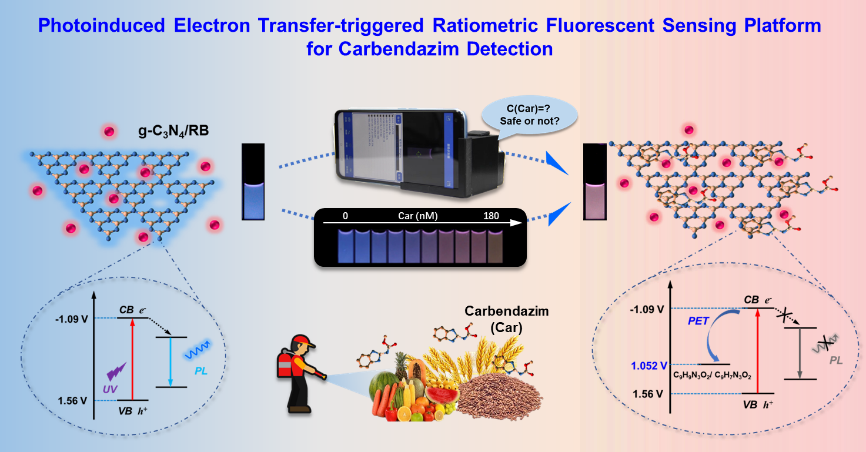
Illustration of the design of the ratiometric fluorescence sensor for carbendazim detection. Image Credit: Qianru Zhang.
Carbendazim, a common pesticide that comes under the benzimidazole family, has been extensively utilized in agricultural production. Since it degrades gradually in nature, the carbendazim residues could be absorbed simply into the body through skin, respiration, or ingestion.
The current common analytical techniques for detecting carbendazim residues are still restricted to immunoassay and laboratory instruments, etc., which generally have a high price, complicated operation, and take a long time. It is of great importance to come up with a new technique for carbendazim detection with high selectivity and sensitivity.
In this study, the novel photoinduced electron transfer-activated g-C3N4 or Rhodamine B sensing system was engineered for selective and visual quantitative detection of carbendazim residues.
The scientists discovered that the carbendazim molecules could be enriched onto the g-C3N4 nanosheet by π-π stacking. Further, the blue-emitting fluorescence of the g-C3N4 nanosheet can be quenched by photoinduced electron transfer, while the orange fluorescence of RB remains unaltered.
Our sensor realized a fast visual response to trace carbendazim residues through sensitive fluorescence changes from blue to purple.
Qianru Zhang, Study First Author, Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The limit of detection is as low as 5.89 nM, far below the utmost residue standard.
In this regard, with the help of 3D printing technology and color recognition, the portable intelligent sensing platform developed by the research group could be employed for the detection of carbendazim in actual samples and displays good anti-interference ability.
This study provides a sophisticated sensing strategy for sensitivity and quick carbendazim detection in the field. However, it also provides new knowledge into other trace analytes’ quantitative analysis.
This study was financially supported by the Research of National Key and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province.
Journal Reference
Zhang, Q., et al. (2023) Photoinduced Electron Transfer-Triggered g-C3N4\Rhodamine B Sensing System for the Ratiometric Fluorescence Quantitation of Carbendazim. Analytical Chemistry. doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05691.